Pathophysiology
Inflammatory arthritis caused by the deposition of uric acid crystals in the joint. Hyperuricemia is defined as urate levels ≥ 6.8 mg/dL.
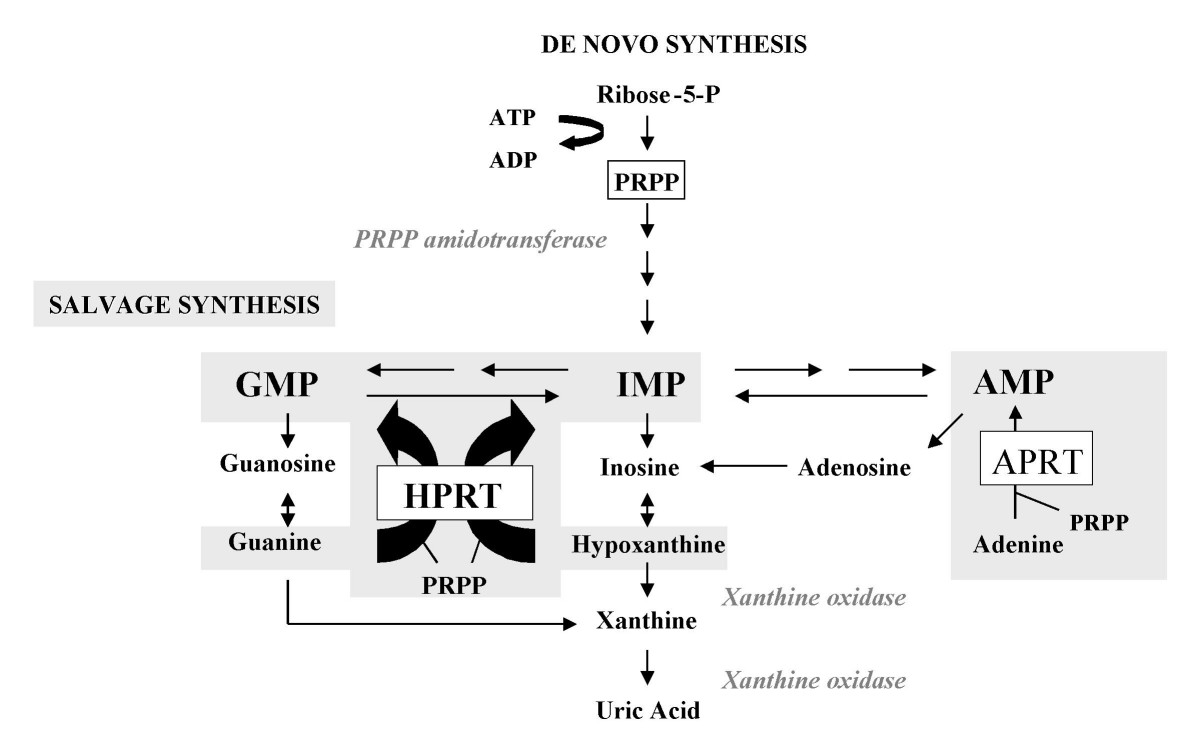
Purine Metabolism
Risk Factors
- Age
- Low kidney function
- Male
- High BP
- Obesity
- EtOH use
SSx
Severe pain and inflammation around tophi (urate deposits), most commonly in the big toe
Treatment
Acute Flairs
- NSAIDs at highest recommended dose until 24hr after SSx resolution
- Indomethacin 50mg PO TID
- Naproxen 750mg then 250mg PO q8hr
- Sulindac (Clinoril) 200mg PO bid
- Colchicine
- Load 1.2 mg PO then 0.6mg 1hr later
- Continue 0.6mg QD or BID 12 hrs later until resolution of attack
- CrCl < 30: Do not repeat treatment w/i 14d, and 0.3mg QD prophylactic dose
- HD: 0.6mg PO x1 do not repeat w/i 14d, and 0.3mg twice weekly prophylactic dose
- SEs
- N / V / D
- Bone marrow suppression, aplastic anemia, and thrombocytopenia
- Myopathy
- Rhabdo
- Inhibits leukocyte migration and phagocytosis via interactions with microtubules
- Comparable to NSAIDs in efficacy
- Best to start w/i 24hr of SSx onset
- GCs
- Most commonly used w/ multiple joint involvement or resistant cases
- Prednisone, methylprednisolone, and triamcinolone all common
- Prednisone 0.5 mg/kg QD x5-10d or 0.5 mg/kg x2-5d then 7-10d taper
- Methylprednisolone 21d dose pack
- Triamcinolone 60mg IM x1 dose then PO prednisone as above, or 2.5-40mg intra-articular x1 dose
- Combine Colchicine and NSAIDs, Colchicine and PO GCs, or Intra-articular GCs and any other treatment
Maintenance
- Indications
- Two or more attacks per year
- Presence of tophi
- Presence of renal stones
- CKD Stage 2 or worse
- Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitors
- Allopurinol 100mg PO QD NTE 800mg QD
- Slowly titrate q2-4wks
- 50mg PO QD w/ CKD 4
- CrCl 10-20: NTE 200mg PO QD
- CrCl 3-10: NTE 100mg PO QD
- CrCl < 3: Consider QOD
- SEs: Rash, pruritus, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, N / V / D, SJS / TEN, eosinophilia, vasculitis
- Screen fro HLA-B*5801 in Asian ethnicities to decrease risk of SJS / TEN
- Febuxostat 40mg PO QD NTE 80mg QD
- No renal adjustments
- Do not initiate or stop during an attack
- Data limited for CrCl < 30 and severe hepatic impairment
- Expensive
- SEs: Rash, N /D, LFT elevations, increased risk of thromboembolism
- CI: Azathiprine, mercaptopurine, or theophylline use
- Monitoring: LFTs at baseline, 2mo, and 4mo
- Allopurinol 100mg PO QD NTE 800mg QD
- Uricosurics (Added to above)
- Inhibition of uric acid reabsorption in the PCT
- Probenecid 250mg PO BID x7d then 500mg BID x14d NTE 2g qd
- Titrate by 500mg q1-2wks as needed
- SEs: Flushing, HA, GI Upset, Kidney Stones, Aplastic anemia / leukopenia
- CIs: Salicylate use, blood dycrasias, uric acid kidney stones, CrCl < 50, acute attack
- Uricase Therapy
- Converts uric acid into allantoin
- Pegloticase 8mg IV Infusion q2wks over 120min
- Pretreat w/ antihistamines and GCs
- SEs: Infusion related events, nephrolithiasis, anaphylaxis, arthralgia, CHF exacerbation, nausea
- CIs: G6PD Deficiency
- Avoid in CHF pts
- Miscellaneous Therapies
- Lesinurad (Zurampic) 200mg PO QD
- Inhibits urate transporter increasing excretion
- Can use with xanthine oxidase inhibitors
- SEs: Acute renal failure (black-box), HA, GERD
- Lesinurad (Zurampic) 200mg PO QD
Prophylaxis
- Colchicine 0.6mg PO QD or BID
- Naproxen 250mg PO BID
- < 10 mg prednisone equivalents QD
Monitoring
- Serum Urate x2-5 weeks during initiation, then q6mo once < 6 mg/dL