Seizure Classification
Focal Szs
Focal Szs are classified as either preserved (simple partial) or altered (complex partial) awareness. Simple Szs can degenerate into complex, and either can evolve into bilateral, generalized, tonic-clonic szs.
- Aware Partial Szs
- Limited Convulsions, No LOC, and Limited Sensory Disturbances
- May Present w/ auras of abdominal discomfort, unpleasant smells, or a sense of fear
- Impaired Awareness Partial Szs
- Present w/ clouding of consciousness, staring, and repetitive motor behaviors
- May also present with autonomic dysfunction (diarrhea, vomiting, etc)
- Auras are common (same SSx as Aware Partial Szs)
- Most common form of focal Sz
Generalized Szs
Generalized Szs can be classified as the following
- Absence
- No Convulsions, Aura, or Post-Ictal Period
- Typical (Petit-Mal Szs): Brief LOC (10-45s) w/ staring or eye flickering, often repetitive
- Atypical: Slower onset than Petit-Mal and more difficult to control
- Myoclonic
- Shock-Like Muscle Contractions
- Isolated location jerking (head, trunk, etc)
- Tonic
- Often occur in children
- Increased rigidity of extensor muscles
- Clonic
- Often occur in children
- Rapid, repetitive motor activity
- Tonic-Clonic (Grand-Mal)
- Cyclical tonic phase (15-30s of muscle rigidity) followed by clonic phase (1-2min of violent jerking)
- Tremor begins to develop in tonic phase as clonic phase begins
- Commonly presents w/ urinary incontinence
- Characteristic of Epilepsy
- Atonic
- Sudden loss of muscle tone
- Status Epilepticus
- Single Sz or Multiple Szs w/o baseline consciousness for ≥ 30min
- Usually begin treatment after > 5min
Post-Ictal States
Post-Ictal states can last from seconds to hours, and depending upon the length of the Sz, age of the patient, use of anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs), and areas of the brain that are affected.
SSx
- Confusion
- Disorientation
- Anterograde Amnesia
Seizure Pathophysiology
An imbalance in Excitatory and Inhibitory Post-Synaptic Potentials leads to the development of a Sz. Excitatory potentials are often caused by AMPA and NMDA receptors (glutamate receptors) leading to Ca influx and depolarization. Hyperpolarization is often mediated by GABA receptors leading to K efflux through both voltage gated and Ca defendant K efflux channels. Tonic phases of Szs are often carried out by loss of GABA mediated inhibition leading to excessive activation by glutamate, and clonic phases/oscillations occur due to the reintroduction of GABA mediation.
Status Epilepticus Managment
Common Triggers
- Prenatal Injury
- Hemorrhage
- Infection
- Trauma
- Tumors
- Cerebrovascular Disease
- Anoxia
- Hyperventillation / Respiratory Alkalosis
- Hypoglycemia
- Sleep Deprivation
- Stress
- DTs
- AED Withdrawal
- Repetitive Light Stimulation
Drug Triggers
- EtOH
- Burpropion
- Theophylline
- Imipenem
- Phenothiazines
- Oral Contraceptives
- Tramadol
- Depressant Withdrawal (Esp EtOH and Benzos)
- Meperidine
- CNS Stimulants
- Memantine
- Heave Metal Toxicity
- Clozapine
Management of Status Epilepticus
- 0-5min
- ABCs
- EEG
- Blood Glucose
- If < 60, give 100mg IV Thiamine and 50mL IV D5W
- CBC w/ Diff
- Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP)
- Toxicology Screen
- 5-20min
- Midazolam IM 10mg if > 40kg or 5mg if 13-40kg (one dose)
- Lorazepam 0.1 mg/kg IV (Max 4 mg/dose) (Max of 2 doses)
- Diazepam 0.15-2 mg/kg IV (Max 10 mg/dose) (Max of 2 doses)
- Phenobarbital 15 mg/kg/dose IV (single dose, not preferred agent)
- Diazepam 0.2-0.5 mg/kg Rectal (Max 20 mg/dose) (not preferred agent)
- Intranasal Midazolam or Buccal Midazolam (not preferred agent)
- 20-40min
- Fosphenytoin 20 mg PE/kg IV (Max 1500 mg PE/dose, single dose) (PE = Phenytoin Equivalents)
- Valproic Acid 40 mg/kg IV (Max 3000 mg/dose, single dose)
- Levetiracetam 60 mg/kg IV (Max 4500 mg/dose, single dose)
- Phenobarbital 15 mg/kg/dose IV (single dose, not preferred agent)
- 40-60min
- Repeat Second Line Therapy (Step 3) OR
- Anesthetic Doses of the following PLUS Continuous EEG
- Thiopental
- Midazolam
- Phenobarbital
- Propofol
Seizure Management
Criteria for Considering D/C of AED
2-5yr Sz free period
Risk Factors for recurrence include:
- < 2 years seizure free
- Onset of seizure after age 12
- History of atypical febrile seizures
- 2-6yr before good seizure control in treatment
- Significant number of seizures (> 30) before control achieved
- Partial seizures (which is the most common type)
- Abnormal EEG throughout treatment
- Organic neurological disorder
- Traumatic brain injury
- Dementia
- Withdrawal of phenytoin or valproate
Medication Therapy
Typical First-Line Therapy by Sz Type
| Sz Class | Typical 1st Line Agents |
|---|---|
| Partial-Onset | Carbamazepine Lamotrigine Levetiracetam Oxcarbazepine Valproate |
| Tonic-Clonic | Carbamazepine Lamotrigine Oxcarbazepine Valproate |
| Absence | Ethosuximide Lamotrigine Valproate |
| Myoclonic | Levetiracetam Topiramate Valproate |
| Lennox-Gastaut | Valproate Lamotrigine |
Drug Interactions
| Enzyme | Substrate | Inducer | Inhibitor |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1A2 | Carbamazepine | Carbamazepine Phenobarbital Phenytoin Primidone |
|
| 2C9 | Brivaracetam Phenobarbital Phenytoin Primidone Valproate |
Carbamazepine Phenobarbital Phenytoin Primidone |
|
| 2C19 | Brivaracetam Lacosamide Phenobarbital Phenytoin Primidone Valproate |
Carbamazepine Phenobarbital Phenytoin Primidone |
Eslicarbazepine Lacosamide Oxcarbazepine Topiramate |
| 2D6 | Clobazam | ||
| 3A4 | Carbamazepine Clobazam Clonazepam Ethosuximide Felbamate Preampanel Tiagabine Zonisamide |
Carbamazepine Clobazam Eslicarbazepine Felbamate Lamotrigine Oxcarbazepine Phenobarbital Phenytoin Primidone Rufinimide Topiramate REDUCE OC EFFICACY |
|
| UGT | Carbamazepine Eslicarbazepine Phenobarbital Phenytoin Primidone |
Valproate |
Contraceptive Use
Contraceptive interactions are primarily mediated through CYP3A4 alterations leading to increased breakdown of the estrogen component of contraceptives. Contraceptives must be used in patients on anticonvulsants, as almost all anticonvulsants are teratogenic. This interaction can be avoided by utilizing progestin-only formulations, high dose estrogen OCs, IUDs, etc.
Phenytoin / Fosphenytoin
- Phenytoin: 20 mg/kg IV w/ a second dose after 10min if needed
- Phenytoin: Maximum Infusion Rate of 50 mg/min IV
- Fosphenytoin: 20 PE/kg IV w/ a second dose after 10min if needed
- Fosphenytoin: Maximum Infusion Rate of 150 PE/min IV
- Phenytoin Limiting SE of Infusion rate is hypotension due to propylene glycol
- Monitor for purple glove syndrome
- Cardiac Monitoring Required
- Oral Dose Conversion
- Adjusted Concentration =
- Albumin and serum concentration must be measured at the same time
- Target Concentration = 10-20 mcg/mL
- High Withdrawal Risk
Valproate
- Load 15-20 mg/kg
- Follow with 15 mg/kg QD titrated to Max 60 mg/kg QD
- IV given in divided doses given Q6H
- IV:PO Conversion is 1:1
- Loading Dose Calculation
- Dose =
- Vd = 0.2-0.3 L/kg
- Target Concentration = 80 mcg/kg (50-125 mcg/mL)
- High Withdrawal Risk
Lamotrigine
| Without UGT Interactions | w/ UGT Inhibitor (Valproate) (Halve Dose) |
w/ UGT Inducer (Carbamazepine, Phenytoin) (Double Dose) |
|---|---|---|
| 25mg QD x14d | 25mg QOD x14d | 50mg QD x14d |
| 50mg QD x14d | 25mg QD x14d | 100mg QD x14d |
| 100mg QD x7d | 50mg QD x7d | 200mg QD x7d |
| 200mg QD | 100mg QD | 400mg QD |
Always re-evaluate lamotrigine dose if offending interaction is started or stopped. Titration schedule must be followed strictly to avoid high risk of SJS/TEN. In pts with prior exposure to lamotrigine higher initial doses may be used.
Medication Table
| Drug | Brand | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Brivaracetam | Briviact | C-V controlled substance; adjunctive therapy for partial-onset seizures, twice daily dosing, dose adjustment for hepatic impairment, 2C19 substrate, injection available (4 day max use), somnolence/sedation, ataxia, fatigue, dizziness, N/V, psychosis, irritability, aggression, depression, rifampin decreases serum concentration of brivaracetam |
| Carbamazepine | Tegretol (IR or XR) Carbatrol Epitol |
Partial/generalized seizures, P450 inducer (including auto-inducing own metabolism), hyponatremia, aplasticanemia, SJS/TEN (HLA-B*1502 testing in patients of Asian descent), DRESS syndrome (HLA-A*3101 testing –Northern European descent (not required, suggested), therapeutic range 4–12 mcg/ml, electrolytes, CBCw/platelets, decreased efficacy of OCs, teratogen – category D (some generics available) |
| Clobazam | Onfi | C-IV controlled substance; 3A4 substrate, weak 3A4 inducer – possible decreased efficacy of OCs; 1,5–benzodiazepine (theoretically less abuse potential); significant withdrawal symptoms if stopped abruptly; indicated only as adjunct for Lennox-Gastaut syndrome |
| Clonazepam | Klonopin | C-IV controlled substance; 3A4 substrate; pregnancy category D, indicated for myoclonic seizures; side effects – anterograde amnesia, paradoxical disinhibited behavior, significant withdrawal symptoms if stopped abruptly, respiratory depression, CNS depression; contraindicated in severe hepatic dysfunction; generic available |
| Eslicarbazepine | Aptiom | Active metabolite of oxcarbazepine; prodrug metabolized to active form; 2C19 inhibitor; SJS/TEN (HLA-B*1502testing in patients of Asian descent (required) and HLA-A*3101 testing of patients of Northern European descent (not required), hyponatremia, blood dyscrasias (not as severe as carbamazepine); partial/generalized tonic clonic |
| Ethosuximide | Zarontin | Indicated only for absence seizures; avoid in renal/hepatic dysfunction; 3A4 substrate; CBC w/diff. & platelets, BMP – leukopenia, eosinophilia, psychiatric/sleep disturbances, aggression; SLE, SJS/TEN (generic available) |
| Felbamate | Felbatol | Boxed warnings – aplastic anemia, hepatic failure – LFTs baseline and frequently thereafter (at least every 3 months), warn patients about signs of hepatic dysfunction, CBC w/ diff. & plts baseline and every 3 months – d/c if signs of bone marrow suppression; most commonly used for Lennox-Gastaut syndrome (generic available) |
| Gabapentin | Neurontin Gralise Fanatrex |
Abuse potential although not a controlled substance; 100% renal clearance; CrCl 30–60 mL/min – max dose 1800 mg/day; not recommended CrCl < 30 mL/min; monitor renal function; sedation, peripheral edema; first-line agent partial/generalized tonic clonic; also used for neuropathic pain(generic available) |
| Lacosamide | Vimpat | C-V controlled substance; partial/generalized tonic clonic; IV dosing available for status epilepticus; 2C19 substrate and inhibitor; caution in cardiac conduction abnormalities – prolongs PR interval –visual disturbances; dizziness, ataxia, somnolence, double vision; idiosyncratic – hepatic impairment, 1st Degree Heart Block |
| Lamotrigine | Lamictal | Broad spectrum anticonvulsant – 1st line agent, SJS/TEN – dose titration required to minimize risk; may decrease efficacy of OCs at higher doses of lamotrigine; blurred vision, drowsiness, dizziness, decreased coordination (generic available – IR dosage form) |
| Levetiracetam | Keppra | Broad spectrum anticonvulsant; IV dosing available for status epilepticus; 1st line agent; renal dosing for CrCl < 50 mL/min; ESRD – 500–1000mg q24hr max, supplement 25–500mg after dialysis; adults with partial seizures – ataxia, abnormal gait; adolescents (most commonly) –psychosis, worsening depression, unusual mood changes (generic available) |
| Lorazepam | Ativan | Not commonly used as an oral dose for maintenance control of seizures (abuse potential); common1st line agent for status epilepticus; significant withdrawal symptoms if taken orally for maintenance treatment and abruptly stopped; CAN be used in hepatic dysfunction |
| Oxcarbazepine | Trieptal Oxtellar XR |
3A4 substrate/inducer; 2C19 inhibitor; SJS/TEN (HLA-B*1502 testing in patients of Asian descent(required)), DRESS syndrome (HLA-A*3101 testing in patients of Northern European descent – not required), hyponatremia (more common than with carbamazepine), blood dyscrasias (less common than with carbamazepine, NOT aplastic anemia); CBC w/differential/platelets, electrolytes (generic) |
| Perampanel | Fycompa | C-III controlled substance; 3A4 major substrate, dosing adjustments if given with 3A4 inducers; boxed warning for serious/life-threatening neuropsychiatric events; use with caution in pts w/ psychosis; gait disturbance, somnolence |
| Fos-/Phenytoin | Dilantin (Fos-) Cerebyx |
Strong P450 and UGT inducer; teratogen – pregnancy category D, therapeutic serum conc 10 – 20mcg/mL (calculate free phenytoin with albumin); boxed warning – cardiovascular events; decreased bone mineral density, SJS/TEN, nystagmus, ataxia, double vision, hepatotoxicy, hirsutism, gingival hyperplasia, alteration of Vit D metabolism; osteoporosis; status epilepticus– fosphenytoin dosed in phenytoin equivalents preferred to reduce risk of arrhythmias, hypotension, purple glove syndrome |
| Phenobarbital | C-IV controlled substance; not commonly used in oral dosing in adults for seizure maintenance, may see in children; status epilepticus dosing for refractory status; pregnancy category D; 2C9 substrate;P450 and UGT strong inducer; LONG half-life; somnolence, cognitive impairment; impaired Ca absorption; can be fatal in overdose (generic available) | |
| Pregabalin | Lyrica | C-V controlled substance; partial/generalized tonic clonic; 100% renal elimination – dose adjustments in CrCl < 60 mL/min; angioedema, PR prolongation; dizziness, sedation, peripheral edema; monitor renal function; more commonly used for neuropathic pain and generalized anxiety disorder |
| Primidone | Mysoline | Metabolized to phenobarbital; Pregnancy category D; strong P450 and UGT inducer; more commonly used to treat essential tremor; monitor LFTs and CBC w/ diff & plts (generic) |
| Rufinamide | Banzel | Lennox-Gastaut or refractory seizures; CI in familial short QT syndrome; DRESS; SJS/TEN; somnolence, fatigue, ataxia, nausea |
| Tiagabine | Gabitril | 3A4 substrate – dose adjustments required for use with strong 3A4 inducers or inhibitors; may cause cognitive impairment; somnolence, tremor; use with caution off-label for patient w/o Sz disorder (ie, as a mood stabilizer for bipolar disorder) and with hepatic dysfunction – may trigger seizures |
| Topiramate | Topamax | 3A4 substrate/inducer – may decrease efficacy of OCs, pregnancy category D, status epilepticus dosing – but is only PO dosing; warnings/precautions – nephrolithiasis, CNS depression, metabolic acidosis, oligohydrosis/hyperthermia; secondary angle-closure gluacoma; visual field defects; cognitive impairment, hyperchloremic non-anion gap metabolic acidosis; monitor urinalysis, BMP (for bicarbonate) q6m dose titrate slowly (generic) |
| Vigabtrin | Sabril | 35% renally cleared, otherwise UGT metabolism; renal dosing for CrCl < 80 mL/min; CI in patients with other risk factors for irreversible vision loss (boxed warning), warnings for peripheral neuropathy, edema, anemia, neurotoxicity; side effects – depression, insomnia, weight gain, permanent loss of peripheral vision |
| Valproate | Depakote | Broad spectrum; use not recommended in pregnancy – neural tube defects/lower IQ in offspring; serum concentration range – 50–125 mcg/mL; status epilepticus dosing available, including loading dose; may cause hyperammonemia, thrombocytopenia, weight gain, N/V, sedation, alopecia, polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) – monitor CBC w differential/platelets, LFTs, serum concentration; watch dispensing – IR capsules, DR tablets, ER tablets, sprinkle capsules(some are generic) |
| Zonisamaide | Zonegran | CI in sulfa allergy; partial/generalized tonic clonic; metabolic acidosis, renal calculi, DRESS syndrome, drowsiness, tremor, weight loss |
Severe Adverse Drug Reactions
Anticonvulsant Hypersensitivity Syndrome
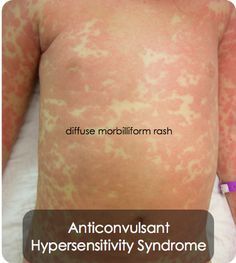
AHS is a severe allergic reaction associated with arene-oxide metabolic intermediate of aromatic drugs. The reaction presents as a diffuse, morbiliform rash. There is some cross reactivity with TCAs because of this. Common offenders include:
- Carbamazepine
- Oxcarbazepine
- Eslicarbazepine
- Felbamate
- Lamotrigine
- Phenobarbital
- Phenytoin
- Zonisamide
Carbamazepine and its derivatives are the most common offenders, and a significantly increased risk of this reaction occurs in patients carrying HLA-B*1502, which is most commonly seen in Asian populations. HLA-A*3101 conveys some risk as well, and is common in those of Northern European descent.
DRESS Syndrome
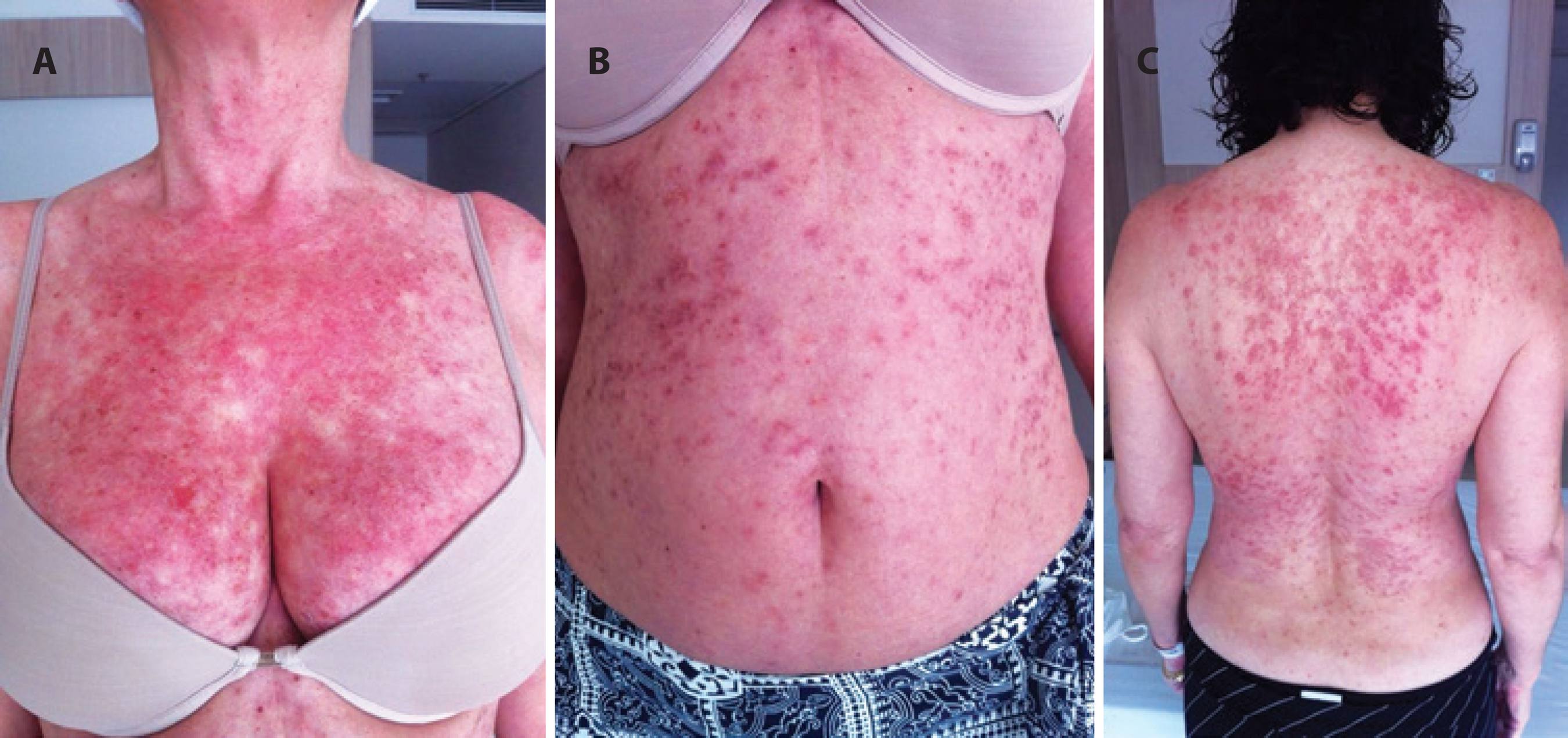
Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms is a life threatening allergic reaction which commonly initially presents with a similar rash to measles. The reaction then progresses to organ dysfunction and multi-system organ failure. DRESS commonly occurs 2-6wks after initiating one of the following:
- Carbamazepine
- Lamotrigine
- Phenobarbital
- Phenytoin
- Valproate
- Zonisamide
HLA-A*3101 (common in Asians and Northern European Populations) is commonly associated with an increased risk of DRESS syndrome. Treat by withdrawing drug and providing supportive care.
Anticonvulsant Withdrawal Syndrome
Anticonvulsant withdrawal refers to the increased risk of Szs associated with abrupt discontinuation of anticonvulsant medications. Common other SSx include:
- Anxiety
- Agitation
- Other Physical Complaints
Anticonvulsant withdrawal syndrome can be prevented by slowly tapering patients off medication. Tapers of the course of a year are appropriate for trial D/C due to lack of Szs. Patients with non-life threatening SEs should be tapered slowly, but can be tapered faster than 1 year. Consider the longest taper medically feasible without undue danger or suffering to the patient.
Pregnancy and Anticonvulsant Medications
Sz frequency increases during pregnancy, and dosing regimens may change. Unfortunately many anticonvulsants are known teratogens such as:
- Carbamazepine
- Clonazepam
- Fos-/Phenytoin
- Phenobarbital
- Primidone
- Topiramate
- Valproate
These medications should not be used in pregnancy if at all possible. Pregnant patients should be supplemented with Folate 5mg QD and consider Vit K 10mg QD in the last month of pregnancy followed by Vit K 1mg IM (for the infant) at birth.
Depression and Epilepsy
Sz disorder pts are at high risk for epilepsy. All anticonvulsants increase risk of suicidal thinking/behavior. Antidepressant therapy carries an increased risk of suicidal thinking/behavior in those < 24yo. Many antidepressants also have CYP interactions to consider. Bupropion should not be used in patients with Sz disorders as it decreases the Sz threshold.
CVD and Anticonvulsants
- QTc Shortening: Rufinamide
- PR Changes: Lacosamide, Pregabalin
- Peripheral Edema: Pregabalin, Gabapentin
- Heart Block: Lacosamide (Caution w/ conduction abnormalities)
- Arrhythmia: Fos-/phenytoin (CI in Heart Block)
Electrolyte, Acid-Base, and Metabolic Abnormalities and Anticonvulsants
- Carbamazepine / Eslicarbaepine / Oxcarbazepine: Hyponatremia and SIADH
- Zonisamide: Metabolic Acidosis and Renal Calculi
- Phenytoin: Decreased levels of Vit D leading to osteoporosis
- Topiramate: CA Inhibitor leading to decreased serum bicarb, metabolic acidosis, and nephrolithiasis
Miscellaneous Therapy
- Ketogenic diets are somewhat effective at reducing Sz frequency, and it is more effective in children
- Vagal Nerve Stimulation
- Deep Brain Stimulation
- Responsive Neurostimulation
- Surgery to remove Sz focus