Coagulation Cascade
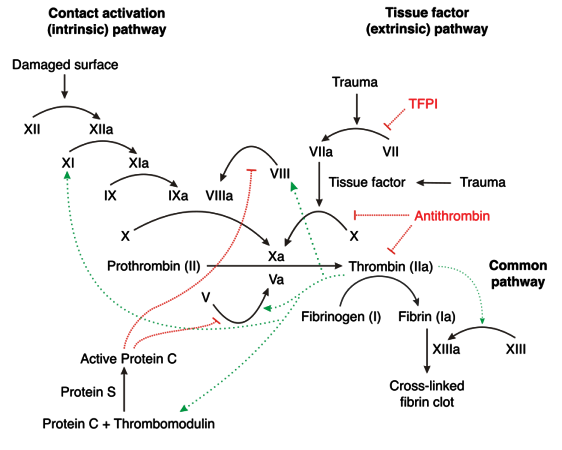
Clotting Factors are produced exclusively in the liver, with the exception of vWF (endothelium, subendothelium, and megakaryocytes) and Factor VIII (liver and endothelium). The cascade begins when Tissue Factor (TF) binds to Factor VII after vascular wall injury exposes extra-vascular tissue. This process begins the extrinisic pathway. The intrinsic pathway is initiated by thrombin (Factor IIa) cleaving Factor XII in response to exposed collagen from damaged endothelial cells. The coagulation cascade is naturally inhibited by Antithrombin III (AT, neutralizes Thrombin, Xa, and IXa), Protein C (neutralizes Va and VIIIa), and Xa (activates Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor).
Lab Tests
| Test | Evaluating | Low | High | Units |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Platelet Count | Bone Marrow | 150 | 450 | k/mm3 |
| PT | Extrinsic Pathway | 12 | 14 | sec |
| INR | Extrinsic Pathway | - | 1.1 | n/a |
| aPTT | Intrinsic Pathway | 26 | 33 | sec |
| PT/INR | aPTT | Anti-Xa Activity | Activated Clotting Time | Thrombin Time | Ecarin Clotting Time | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Warfarin | +* | +/- | - | + | - | No sig. Data |
| UFH | - | +* | + | +* | + | - |
| LMWH | - | +/- | +* | +/- | + | No sig. Data |
| Fondaparinux | - | +/- | +* | - | - | No sig. Data |
| Rivaroxaban | + | +/- | + | +/- | - | - |
| Edoxaban / Apixaban | +/- | +/- | + | No sig. Data | - | - |
| Dabigatran | +/- | + | +/- | - | +* | +* |
(* Preferred Test, + Higher Values, - No Effect, +/- Inconsistent Effect)
Anticoagulant Classes
- Vitamin K Antagonists
- Warfarin
- Factor Xa Inhibitors
- Direct: Rivaroxiban, Apixaban, and Edoxaban
- Indirect: Unfractionated Heparin, LMWH (Enoxaparin / Daltaparin), Fondaparinux
- Direct Thrombin Inhibitors
- Dabigatran
Heparins and Heparin-Like Drugs
Pharmacology
MOA: Stabilization of the Anti-Thrombin - Thrombin and Anti-Thrombin - Factor Xa complexes, decreasing coagulation (Heparin stabilizes both, LMWHs preferentially stabilize the Xa interaction)
Adverse Effects: Hemorrhage, HIT (fondaparinux has no risk of HIT), Osteoporosis
HIT
| T | MOA | Time | Platelets | Clinical Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type I | Platelet Aggregation | < 2d | ~100k | Low |
| Type II | Ig - Platelet Complexes | 5-10d w/o prior exposure | < 50% Baseline | Life-Threatening |
More commonly caused by heparin than LMWHs, D/C immediately and CI further use. Avoid by starting enoxaparin. If HIT II occurs, switch to fondaparinux.
Warfarin
MOA: Inhibition of Post-Translational Modification of Factors II (Prothrombin), VII, IX, and X along with Proteins C and S via inhibition of Vitamin K Reductase (which regenerates reduced vitamin K for post-translational modificaiton)
Warfarin takes approximately 3-5 days to reach maximal effect due to the half-lives of the respective clotting factors
- Prothrombin (factor II): 60-100 hours
- Factor VII: 4-6 hours
- Factor IX: 20-30 hours
- Factor X: 24-40 hours
Protein C and S have significantly shorter half-lives, and initiation of warfarin therapy can temporarily lead to an increase in coagulability. This can lead to ischemia and Warfarin Induced Necrosis.
Warfarin is a mix of S and R enantiomers, the S enantiomer being 5x more effective at inhibiting Vit K Reductase.
Dosing
Dosed to reach a goal INR of 2-3 for prophylaxis or treatment of VTE, treatment of PE, prevention of symbolic emboli, antiphospholipid antibody syndrome, and mechanical aortic valve. A target of 2.5-3.5 is used for mechanical mitral valves or to prevent a reccurent MI.
Initial dosing is typically 5mg daily, but healthy outpatients can be given a loading dose of 10mg x2d. Doses should be adjusted weekly, and the total weekly dose should be adjusted, not the daily dose. Patients which may require a dose smaller than 5mg include:
- > 60 years old (elderly)
- Debilitated
- Malnourished
- Congestive heart failure
- Liver disease
- Concomitant medications (check for interactions)
- High bleeding risk
- Genetic factors
Duration of Therapy
| Indication | Duration |
|---|---|
| Reversible Risk Factor | 3mo |
| Idiopathic DVT | ≥ 3mo, re-evaluate and consider up to 1yr |
| DVT + Cancer | LMWH for 3-6mo then warfarin or LMWH indefinitely or until cancer resolves |
| Multiple Events | Lifelong therapy, consider ≥ 3mo if high bleeding risk |
Dosing Adjustments
The 5 D’s of Warfarin Adjustments
- Drugs
- Diseases
- Doses (Missed Doses)
- Diet (Green Vegetables)
- Drink (EtOH)
- Bleeding
Goal INR 2-3
| INR | Dose Adjustment |
|---|---|
| <2 | Increase Dose By 5-15% |
| 3.1-3.5 | Decrease Dose By 5-15% |
| 3.5-4 | Decrease Dose By 10-15% and Hold 0-1 Dose |
| >4 | Decrease Dose By 10-15% and Hold 0-2 Dose |
Goal INR 2.5-3.5
| INR | Dose Adjustment |
|---|---|
| <2.5 | Increase Dose By 5-15% |
| 3.6-4 | Decrease Dose By 5-15% |
| 4.1-4.5 | Decrease Dose By 10-15% and Hold 0-1 Dose |
| >4.5 | Decrease Dose By 10-15% and Hold 0-2 Dose |
Monitoring
Therapy Initialization
| Method | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Flexible | Daily x4d then w/i 3-5d |
| Average Daily Dose | w/i 3-5d, then w/i 1wk |
| After Hospital Discharge | w/i 3-5d if stable, w/i 1-3d if unstable |
| First Month | Weekly |
Maintenance
| Situation | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Dose Held Today | w/i 1-2d |
| Dose Changed Today | w/i 1-2wks |
| Dose Change ≤ 2wks ago | w/i 2-4wks |
| Routine Follow-Up Stable Pt | q4-6wk |
| Routine Follow-Up Unstable Pt | q1-2wks |
| Stable ≥ 6mo | q12wks |
Common Interactions
NSAIDs can increase bleeding but do not increase INR
Increased INR
- Acute Alcohol
- Amiodarone
- Anabolic Steroids
- Bactrim
- Cimetidine
- Ciprofloxacin
- Erythromycin
- Fluconazole
- Isoniazide
- Liver Disease
- Metronidazole
- Propafenone
Decreased INR
- Chronic Alcohol
- Carbamazepine
- Cholestyramine
- Rifampin
- Vit K Containing Foods
Consider empric adjustments of 5-15%
Warfarin Overdose Managment
- INR 4.5-10 w/o evidence of bleeding
- Monitor
- INR > 10 w/o evidence of bleeding
- 5mg PO Vit K
- Major Bleeding
- PCC or FFP (PCC Prefered), Vit K (5-10mg) can be added
- Check INR before administration and 30-60min after of PCC
Therapy Dose Time to Onset Vit K (PO) 5mg w/i 24hr Vit K (IV) NTE 1 mg/min w/i 4-6hr FFP 10-15 mL/kg Rapid, but partial correction PCC 30 IU/kg w/i 10-15min
DOACs
Dosing is condition-specific, and can be reviewed in the DVT article
Xa Inhibitors
- Apixaban (Eliquis)
- Rivaroxaban (Xarelto)
- Edoxaban (Savaysa)
Thrombin Inhibitors
- Dabigatran (Pradaxa)
- Argatroban
Dosing
Post-Op Prophylaxis
| Dabigatran | Rivaroxaban | Apixaban | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dose | Day of Surgery: 110mg x1 (1-4hr post-op) Not Day of Surgery: 220mg QD x28-35d |
Hip: 10mg QD x35d Knee 10mg QD x12d 6-10hr post-op |
Hip: 2.5mg BID x35d Knee 2.5mg BID x12d 12-24hr post-op |
| Renal Adj. | CrCl ≤ 30, no evidence | CrCl ≤ 30, no evidence | CrCl ≤ 30, no evidence |
Non-Valvular A-Fib
| Dabigatran | Rivaroxaban | Apixaban | Edoxaban | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dose | 150mg BID | 20mg QD | 5mg BID | 60mg QD |
| Renal Adj. | CrCl 15-30: 75mg BID | CrCl 15-30: 15mg QD | 2 of the following: SCr ≥ 1.5, Age ≥ 80, or Wt ≤ 60kg get 2.5mg BID HD Pts: 5mg BID unless above criteria are met, then reduce |
CrCl 15-50: 30mg QD Not for use if CrCl > 95 |
DVT / PE Treatment (3mo if provoked, 3-12+mo if unprovoked)
| Dabigatran | Rivaroxaban | Apixaban | Edoxaban | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dose | 150mg BID | 15mg BID x3wks then 20mg QD | 10mg BID x7d then 5mg BID | 60mg QD |
| Renal Adj. | CrCl < 30: No Data | CrCl < 30: Avoid | CrCl < 25 or SCr > 2.5: No evidence | CrCl 15-50: 30mg QD ≤ 60kg: 30mg QD |
| Notes | Requires 5-10d parenteral anticoagulation | Requires 5-10d parenteral anticoagulation |
Secondary DVT / PE Prophylaxis (May D/C after 6mo)
| Rivaroxaban | Apixaban | |
|---|---|---|
| Dose | 20mg QD | 2.5mg BID |
| Renal Adjustment | CrCl < 30: Avoid | CrCl < 25 or SCr > 2.5: No evidence |
VTE Prophylaxis
| Betrixaban | |
|---|---|
| Dose | 160mg load then 80mg QD x35-42d |
| Renal Adjustment | CrCl 15-30: 80mg load then 40mg QD x35-42d |
| Note | Lasts > 72hr after D/C |
References
- Coagulation Cascade Image Available at http://upload.medbullets.com/topic/111004/images/750px-coagulation_full.svg.jpg